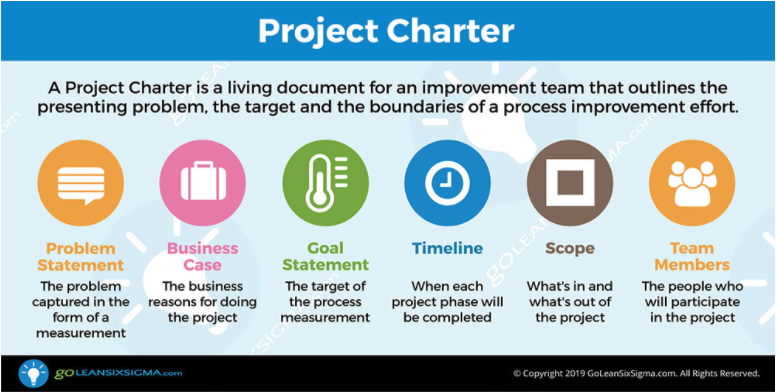
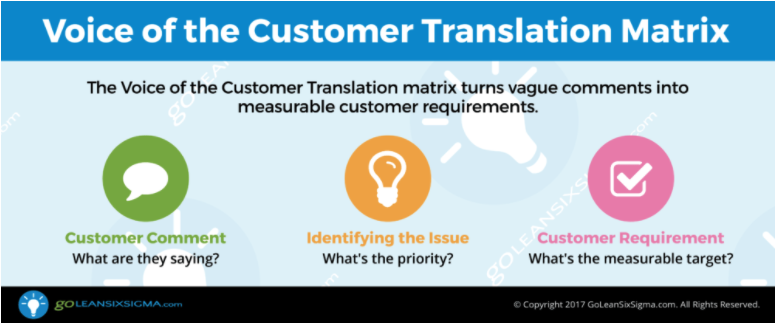
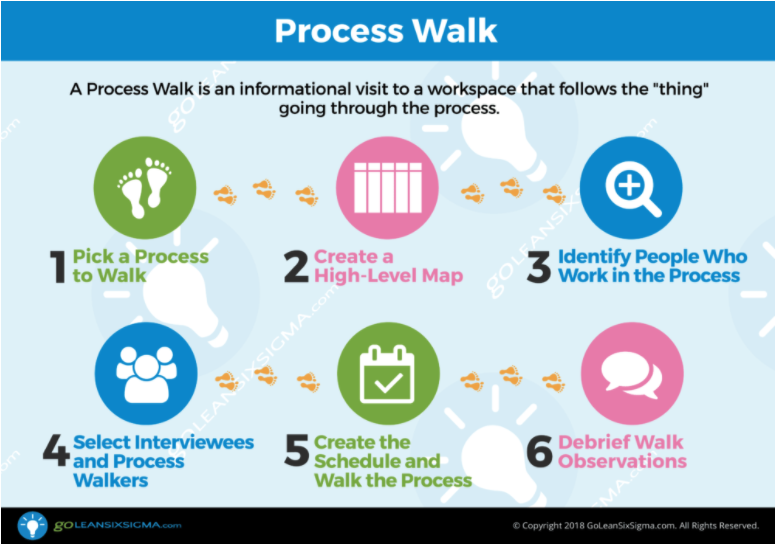
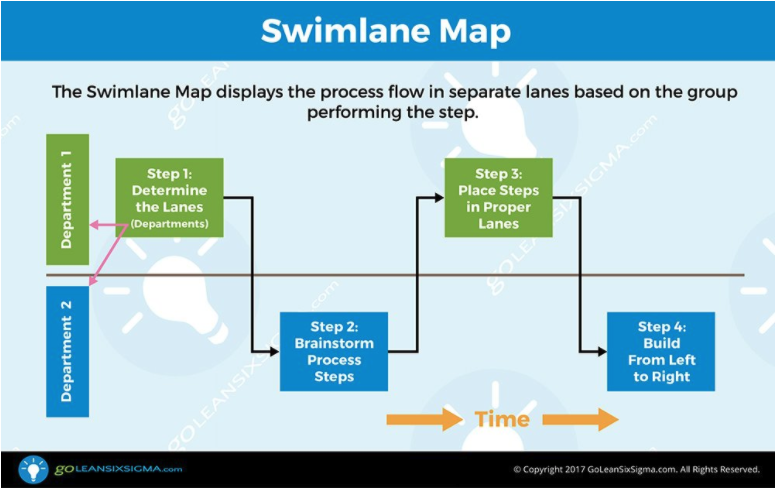
Welcome!
The DMAIC Tollgate Checklist is a great way to guide your improvement efforts. If you're new to process improvement, here is some helpful info.
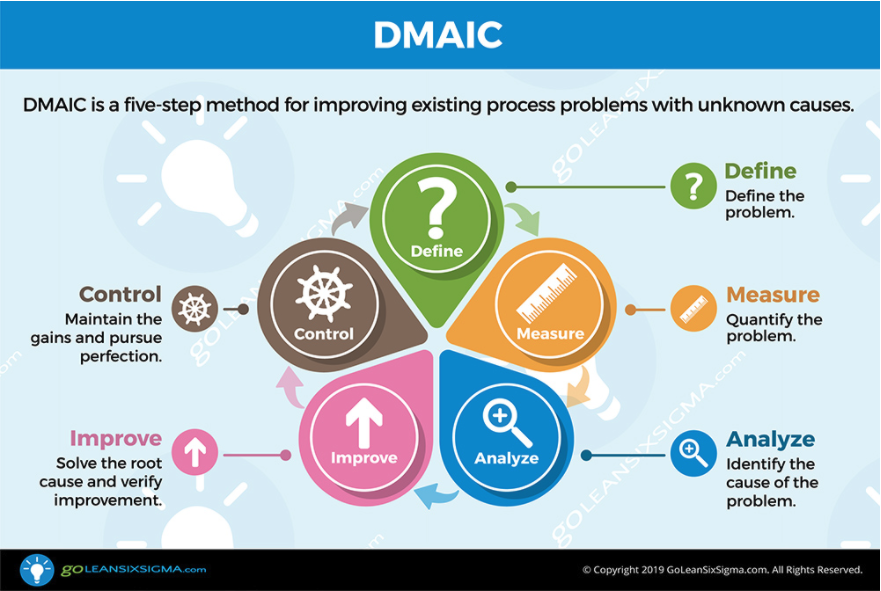
What's DMAIC? DMAIC is a five-step method for improving existing problems with unknown causes. It's part of the Six Sigma system of continuous improvement that was developed by Bill Smith and Mikel Harry of Motorola during the 1980s. Like other process improvement methods it follows the Scientific Method but puts an emphasis on using data to get to the root of process issues.
DMAIC stands for:
- Define: Define the problem
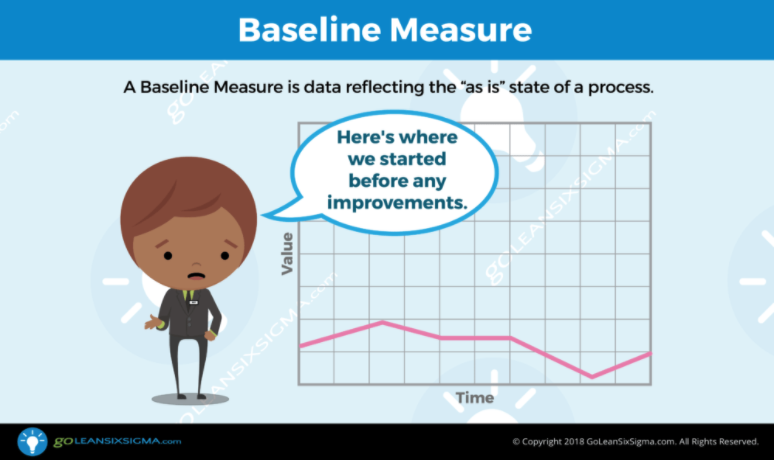
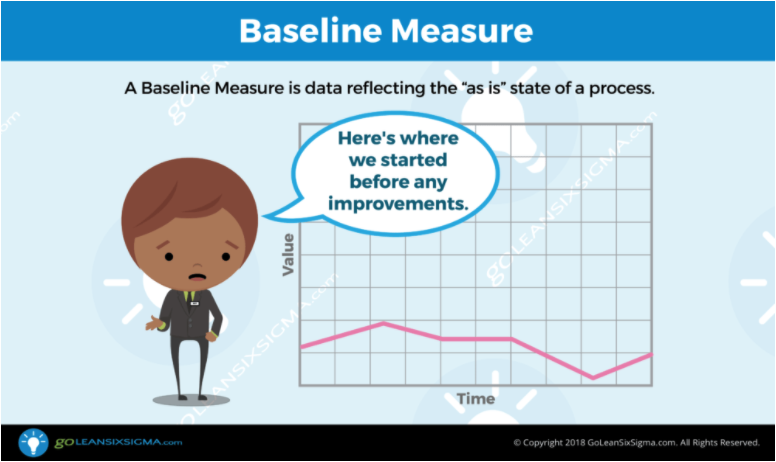
- Measure: Quantify the problem
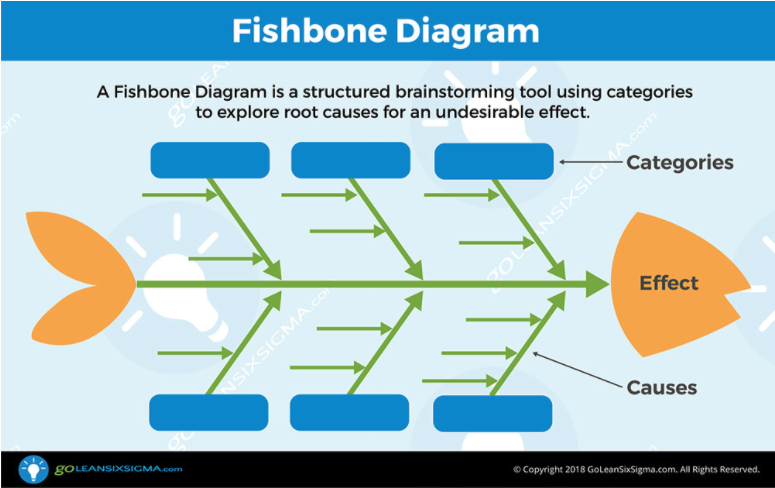
- Analyze: Identify the cause of the problem
- Improve: Solve the root cause and verify improvement
- Control: Maintain the gains and pursue perfection
DMAIC is best for the following types of issues:
- Existing process problems with unknown causes
- Process issues that delay products and services
- Processes that are not meeting customer requirements
- Processes that are producing defective products and services
- Processes overburdened with rework
- Processes that result in customer complaints
You can use the checklist to guide your improvement project, you can mine each task to download helpful templates, and you can watch the embedded videos for some deep dives on how to overcome common challenges.
Some tips on using the template:
- The list on the left represents the tasks to be completed for a DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve & Control) process improvement project
- You can change the checklist name if you like (double click the "Shared Checklist" name)
- It's a good idea to bookmark this link so it's easy to come back to
- Completing all the tasks will complete the checklist..and your project!
- If you'd like your own Process Street account, you can set up a trial access for free
Enjoy!
Your friends at GoLeanSixSigma.com