How this template works
This template is designed to be used to perform a self-audit in accordance with the ISO 9004:2018 standards.
Self-auditing can clearly outline a high-level view of the performance of an organization, and the effectiveness of its management systems.
It can also help to identify areas that are in need of improvement and determine which of these areas should be prioritized, in accordance with business goals or regulatory standards.
Self-audits, as well as audits in general are used to assess whether or not certain aspects of management systems are indeed performing effectively, as defined against standards such as ISO or an organization's own internal objectives.
Self-auditing should be used to discover potential for innovation and continuous improvement, utilizing the output of the audit, usually in the form of clearly outlined strengths, weaknesses, risks, and opportunities for improvement.
Progress over time should also be factored in, on occasion of repeat audits.
This checklist provides an extensive framework for improvement based on the principles outlined in this quality management guidance document. It can be used as is, or edited and customized to suit your specific needs.
Each task employs five levels with which to assess audit outcome, which can be extended to include additional levels or otherwise customized as needed.
Guidelines for success
The following guidelines can be observed in order to ensure effective, efficient, and sustained success of an organization:
- Prioritizing and fulfilling the needs and expectations of interested parties
- Adequately collecting and assessing metrics of performance within the organization
- Constantly seeking to identify and implement improvements across the organization
- Utilizing policies, strategies, and objectives to further business goals
- Effectively and efficiently managing resources with regard to business processes
- Enforcing a company culture based on trust, transparency, and worker empowerment
- Establishing and maintaining beneficial relationships with relevant interested parties where possible, and constantly seeking to develop new beneficial relationships.
Performance can be reviewed against the criteria outlined here and in this checklist, ultimately identifying current "maturity" levels with the goal of outlining strengths, weaknesses, risks, and opportunities.
Additional resources
In addition to this resource, we also have the following ISO-related templates in the form of a quality management system mini-manual blueprint, and a fully fleshed-out version of that blueprint:
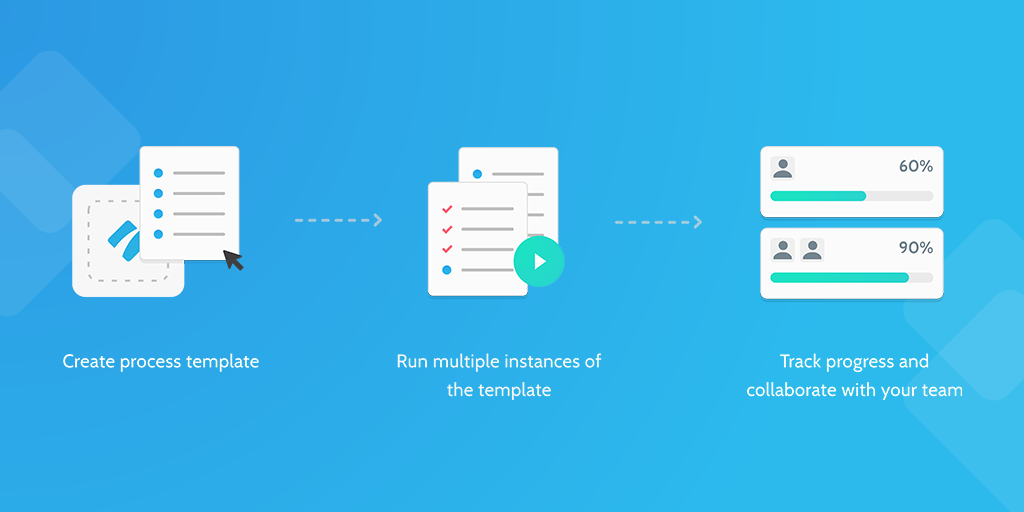
How Process Street works
Process Street is a tool for managing and running processes in an organization.
With Process Street, you can quickly and easily create, edit and deploy your processes.