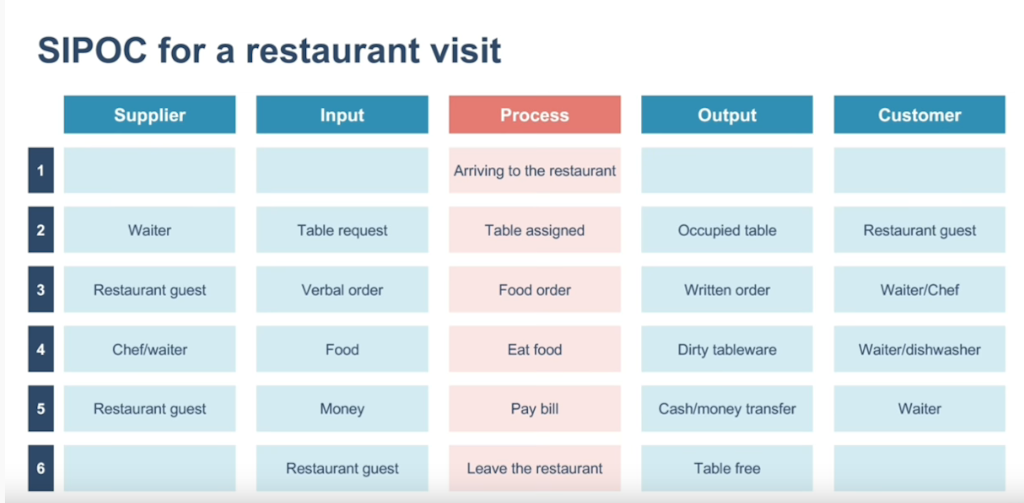
A SIPOC diagram is a tool that helps identify all relevant elements of a process improvement project. Use this tool to define complex processes that might not be well scoped, typically employed at the Measure phase of the Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology.
SIPOC is a tool that is usually used in the Measure phase of the Six Sigma DMAIC project. It can also be used to analyze the different processes in a working system.
SIPOC is an acronym for:
- Supplier
- Input
- Process
- Output
- Customer
The purpose of the SIPOC diagram is:
- To identify the overall processes in the work system.
- To provide an overall perspective.
- Support the definition, structuring, and scoping of complex work systems.
- Highlight possible problems or weaknesses in the processes of the work system.
The SIPOC diagram provides answers to the following questions:
- What is the start and endpoint of the work system?
- What are the essential steps of the work system?
- What are the main inputs and outputs?
- Who are the key customers (internal and external)?
- Who are the key suppliers (internal and external)?
- What are the customer demands?
How to use this checklist
At the beginning of this checklist, you will be presented with a set of specialized questions given as form fields. You are required to populate each form field with your data.
This checklist is structured as per the recommended order of approach by Bzhwen A Kadir to SIPOC. Starting with the identification and documentation of business processes, as opposed to what the acronym suggests. From each process, outputs can be specified, customers for the output determined, needed inputs identified, and supplier information can be gathered.
At the end of each stage, your supervisor/manager will review your work using Process Street's approvals feature. The resulting information is then used to make process improvements. The best way to apply the results will depend on the nature of the system.
Features used in this template include:
- Stop tasks - To ensure task order.
- Dynamic due dates - To make sure your initiative is reviewed on time.
- Role assignment - To delegate tasks within your team ensuring your supervisors are appropriately assigned to the review tasks.
- Approvals - Tasks can be accepted, rejected, and rejected with comments.