Get started quickly, see results immediately, no code needed.
A Complete Guide to the Asset Management Process (+ Free Templates)
Are you looking to streamline your asset management process but not sure where to start?
Asset management involves tracking, maintaining, and optimizing an organization’s physical and digital assets. From equipment and vehicles to software and intellectual property, effective asset management can help businesses improve productivity, reduce downtime, and ensure compliance with regulations.
However, many organizations struggle with managing their assets effectively due to a lack of proper processes and tools. With the right tools and strategies, you can optimize your asset management process and achieve better results.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the asset management process step by step, providing you with valuable insights, best practices, and free templates to help you improve your asset management practices.
Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, this guide will help you optimize your asset management process and achieve better results.
- What is Asset Management?
- Types of Asset Management
- Challenges of Managing Assets
- Stages of the Asset Management Process
- Benefits of Automating the Asset Management Process
- The Best Asset Management Tools
- Best Practices for Using Asset Management Software
- Key Features of Asset Management Process Automation Software
What is Asset Management?
Asset management is the systematic approach to managing and maximizing the value of a company’s assets. This includes both tangible assets, such as physical property, equipment, and machinery, as well as intangible assets, such as intellectual property, brand value, and customer relationships.
Effective asset management involves a range of activities such as:
- Planning
- Optimizing
- Acquisition
- Operation
- Maintenance
- Disposal of assets
It aims to ensure that resources are utilized efficiently, risks are minimized, and the overall performance and profitability of the organization are enhanced. By implementing robust asset management strategies, companies can streamline their operations, reduce costs, increase productivity, and ultimately achieve their long-term goals and objectives.
The 4 Phases of Asset Lifecycle Management
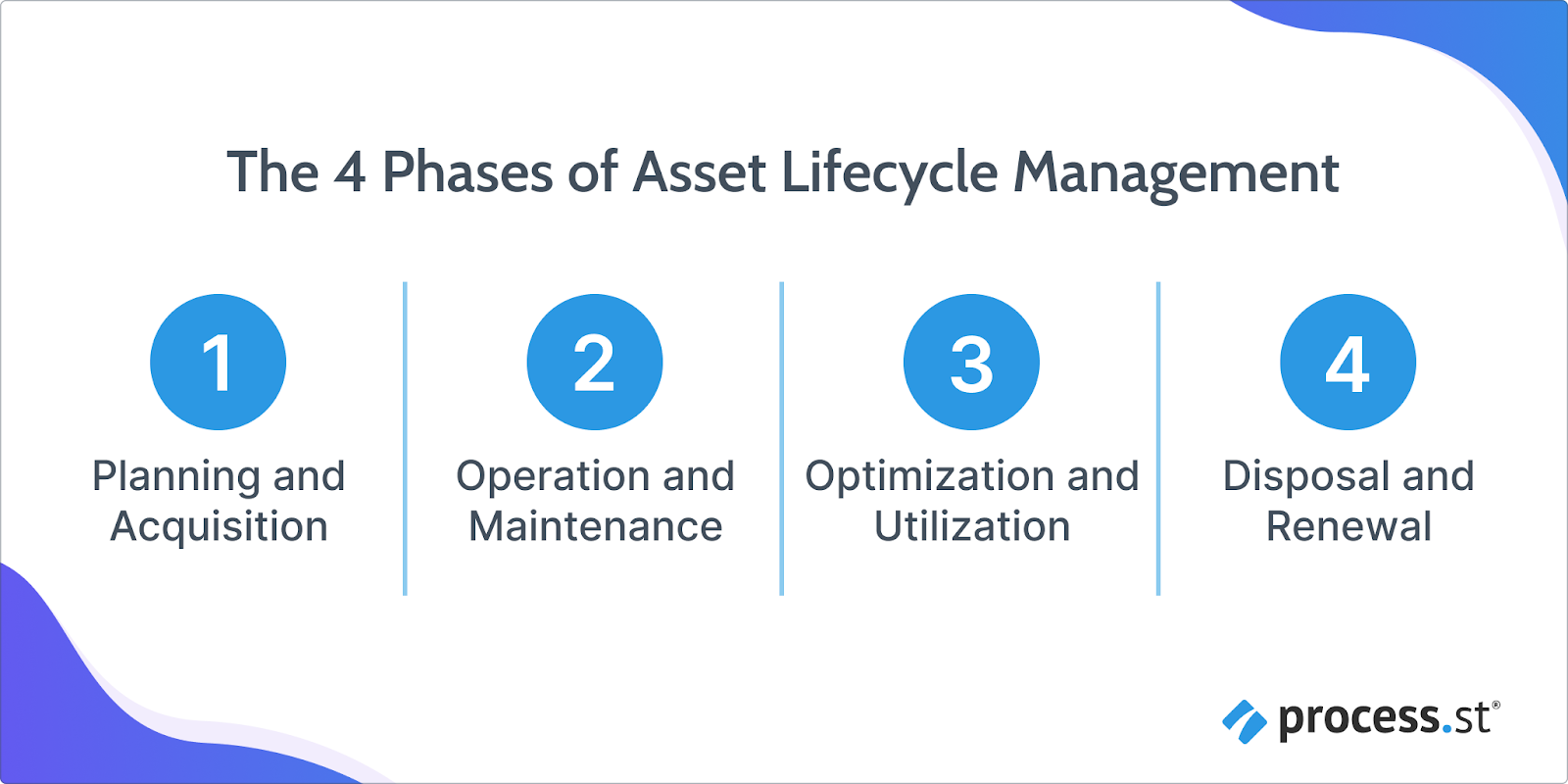
Asset lifecycle management consists of four phases. These are:
- Planning and Acquisition: This phase involves identifying the need for a new asset, securing budgeting and funding, defining specifications, evaluating options, selecting the most suitable asset, and completing the procurement process through negotiation and purchase.
- Operation and Maintenance: Focused on ensuring the asset is effectively deployed and maintained, this phase includes deploying and installing the asset, training personnel, establishing regular maintenance schedules, and continuously monitoring performance to ensure efficiency.
- Optimization and Utilization: This phase emphasizes maximizing asset performance and utility through regular performance analysis, implementing upgrades and improvements, managing costs effectively, and optimizing asset usage to minimize downtime and ensure continuous productivity.
- Disposal and Renewal: In this final phase, an end-of-life assessment determines when the asset should be decommissioned. The asset is then safely removed from operation and disposed of responsibly while renewal planning begins to acquire a new asset, restarting the lifecycle process.
Types of Asset Management
Asset management involves the systematic and strategic management of assets to optimize their value and performance. There are various types of asset management. Here are the 5 more common:
Physical Asset Management
Focuses on managing tangible assets such as machinery, equipment, buildings, and infrastructure. It involves the planning, acquisition, maintenance, optimization, and disposal of physical assets to ensure they provide maximum value and efficiency throughout their lifecycle.
Financial Asset Management
Involves managing financial assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment vehicles. This type of asset management aims to grow and protect wealth through strategic investment decisions, portfolio management, risk assessment, and financial planning.
Infrastructure Asset Management
Deals with the management of infrastructure assets like roads, bridges, water supply systems, and electrical grids. It focuses on maintaining and optimizing these critical public and private infrastructures to ensure they provide reliable services, meet regulatory requirements, and support economic growth.
IT Asset Management
Involves managing an organization’s IT assets, including hardware, software, networks, and data. IT asset management aims to maximize the value of IT resources, ensure compliance with licensing agreements, enhance cybersecurity, and support efficient IT operations and service delivery.
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
Encompasses the comprehensive management of all assets within an organization, integrating physical, financial, infrastructure, and IT asset management. EAM focuses on optimizing asset performance, reducing costs, enhancing asset reliability, and aligning asset management strategies with organizational goals and objectives.
Challenges of Managing Assets
Managing assets in a business presents numerous challenges that can impede efficiency and effectiveness. Some of these challenges include:
Manual Data Entry
Managing assets in a business presents numerous challenges that can impede efficiency and effectiveness. One major pain point is the reliance on manual data entry, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. This labor-intensive process increases the risk of inaccuracies and can lead to asset mismanagement.
Lack of Structured Asset Management Process
Another challenge is the lack of a structured asset management process. Without proper organization, assets may be scattered or misplaced, making it difficult to track and locate them when needed. This can result in unnecessary costs and delays in operations.
Inadequate Authority
Inadequate authority is also a challenge. When there is a lack of centralized control or decision-making power, it becomes challenging to ensure compliance with asset management protocols and policies. This can lead to inconsistencies or negligence in handling assets, compromising their security and value.
Poor Change Management
Furthermore, poor change management poses difficulties in asset management. If there is a lack of proper procedures and communication channels, implementing changes or upgrades to assets can be disruptive and disjointed, causing confusion and resistance from employees.
Absence of Tracking and Reporting Mechanisms
Lastly, the absence of tracking and reporting mechanisms creates challenges in assessing the status and performance of assets. This lack of visibility hampers decision-making and the ability to identify areas for improvement or investment.
Stages of the Asset Management Process

The asset management process involves several stages to ensure that assets are effectively managed within an organization.
By following these stages and using structured templates mapping out the various associated tasks, organizations can effectively manage their assets throughout their lifecycle, ensuring they provide maximum value and support organizational objectives.
1. Asset Planning
This stage involves identifying asset needs, setting goals, and creating a strategic plan for asset management. It includes determining the required assets, budgeting, and aligning asset management strategies with organizational objectives.
Templates:
- Asset Management Plan Template: This asset management plan template outlines tasks for asset identification, age and condition tracking, performance assessment, maintenance strategy, risk evaluation, and management plans with approvals.
- Financial Analysis Template: This financial analysis template details the financial planning for acquiring, maintaining, and disposing of assets.
2. Asset Acquisition
This stage includes the processes of procuring assets, from selecting vendors to finalizing purchase agreements. It ensures that the right assets are acquired at the right price and terms.
Templates:
- Digital Asset Management RFP Template: This digital asset management RFP template provides a structured process for companies to use to solicit bids from potential vendors.
- Purchase Order Workflow Template: The purchase order workflow template documents the order details, including specifications, quantities, and prices.
- Vendor Evaluation Criteria Checklist: This vendor evaluation criteria checklist assists in assessing and selecting the best vendor based on predefined criteria.
3. Asset Deployment
In this stage, acquired assets are installed, configured, and made operational. It includes integrating assets into existing systems and training staff on their use and maintenance.
Templates:
- Software Deployment Checklist: This software deployment checklist ensures all steps when deploying new software in the organizational structure.
- Training Schedule Template: This training schedule template organizes training sessions for staff on asset usage and maintenance.
4. Asset Operation and Maintenance
This stage involves the day-to-day operation and maintenance of assets to ensure they function efficiently and effectively. It includes regular inspections, servicing, and repairs.
Templates:
- Equipment Maintenance Planner Template: This equipment maintenance planner template outlines routine maintenance activities and timelines.
- Quality Inspection Report Template: This quality inspection report template documents the results of regular asset inspections and identifies any issues that need attention.
5. Asset Performance and Optimization
This stage focuses on monitoring and analyzing asset performance to identify areas for improvement. It involves implementing upgrades and optimizations to enhance asset efficiency and extend their lifespan.
Templates:
- Performance Report Template: This performance reporting template tracks and reports on key performance indicators (KPIs) for assets.
- Lifecycle Management Plan Template: This lifecycle management plan template details strategies for improving asset performance and efficiency over its lifecycle.
6. Asset Disposal and Renewal
In this final stage, assets that have reached the end of their useful life are decommissioned and disposed of responsibly. It also involves planning for the acquisition of new assets to replace those disposed of.
Templates:
- Fixed Asset Management Template: This fixed asset management template outlines the steps to streamline the identification, tracking, and reporting of assets.
- Disposal Checklist Template: Ensures all aspects of asset disposal are addressed, including environmental considerations.
- Asset Management Plan Template: This asset management plan template details all the stages of asset management and outlines the steps for managing an asset from the asset planning stage to the asset disposal and renewal stage.
Benefits of Automating the Asset Management Process
Automating the asset management process offers numerous benefits that can significantly improve organizational operations.
Streamlining Tasks
Automating the asset management process significantly streamlines tasks by reducing manual efforts and eliminating human errors. This not only saves valuable time but also allows employees to redirect their focus toward more critical activities. By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, such as data entry and tracking, organizations can increase efficiency and productivity.
Enhancing Decision-Making
Automation enhances decision-making by providing real-time and accurate data. Managers can access comprehensive reports and analyses, enabling them to make informed decisions quickly. This improves the overall decision-making process and allows organizations to proactively identify and address challenges and risks.
Prolonging Asset Life
Automation helps to prolong the life of assets through effective maintenance and monitoring. By utilizing automated systems, organizations can track the condition and performance of assets, enabling them to schedule regular maintenance and detect potential issues early on. This maximizes the lifespan of assets and reduces the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Meeting Consumer Demands
Automation aids in meeting consumer demands by improving responsiveness. With automated systems in place, organizations can quickly adapt to changes in customer preferences and supply chain dynamics. This ensures that products or services are delivered on time, fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Improving Emergency Responses
Automation improves responses to emergencies or unexpected risks. By automating the asset management process, organizations can set up alerts and triggers that notify them of any potential emergencies, enabling them to take immediate action. This reduces downtime, minimizes damages, and enhances overall risk management.
The Best Asset Management Tools
Process Street
Process Street is a powerful platform designed to create and manage workflows, checklists, and standard operating procedures (SOPs) effectively. It streamlines and automates business processes, resulting in greater efficiency and productivity.
Key Features:
- Workflow and Checklist Creation: Allows for the creation of workflows and checklists, ensuring tasks are completed consistently and accurately. Workflows outline the steps and actions required to complete a process, while checklists provide a predefined set of instructions or procedures.
- Centralized Process Documentation: Digitizes and centralizes all process documentation, making it easy to manage and update SOPs. This ensures employees have access to the most up-to-date information, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
- Task Management: Features for assigning responsibilities, setting due dates, and tracking progress. This helps with prioritization and accountability, ensuring tasks are completed on time.
- Integration and Collaboration: Integrates with various other tools and software for seamless collaboration and data sharing. Collaborative features enable multiple users to work together on the same document, promoting teamwork and efficient communication.
- Reporting Capabilities: Provides insights into process performance and areas for improvement. These reports help organizations optimize their processes and enhance overall efficiency.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use interface that allows for customization of templates and workflows to meet specific business needs. This customization ensures the tool can adapt to various requirements.
IBM Maximo
IBM Maximo is a comprehensive enterprise asset management (EAM) solution designed to help organizations effectively manage their assets, including equipment, facilities, and infrastructure. It offers a wide range of features and functionality to streamline asset maintenance processes, improve operational efficiency, and support proactive asset management.
Key Features:
- Streamlined Asset Maintenance Processes: IBM Maximo allows users to schedule and track work orders, manage inventory, and perform preventive maintenance, ensuring assets are maintained efficiently and downtime is minimized.
- Work Order Management: Users can create, assign, and monitor work orders, enabling better planning and execution of maintenance tasks.
- Inventory Management: Maximo provides tools to manage spare parts and inventory, ensuring that the necessary components are available when needed.
- Preventive Maintenance: The software supports the scheduling of regular maintenance activities to prevent asset failures and extend asset lifespan.
- Geospatial Mapping and Visualization: Although it has some issues, Maximo’s spatial add-in allows for the incorporation of geospatial data, enabling better visualization and management of asset locations.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: IBM Maximo is evolving to include advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable predictive maintenance and optimize asset management processes further.
SAP ERP Suite
The SAP ERP Suite is a comprehensive solution for enterprise asset management that offers a range of key features and advantages. It has evolved into a complete set of tools that seamlessly manage materials, assets, and costs in one convenient platform. This suite helps organizations streamline and automate their asset management processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Key Features:
- Streamlining and Automating Asset Management Processes: The SAP ERP Suite provides businesses with the tools needed to manage all aspects of their assets, from procurement and inventory management to maintenance and repair. Centralizing these processes within one solution improves efficiency and reduces costs.
- Real-Time Asset Tracking: Advanced functionality allows businesses to effectively track and monitor their assets in real time. This ensures that organizations have up-to-date information on asset status and location.
- Predictive Maintenance: The suite includes tools for predictive maintenance, helping organizations anticipate and address potential issues before they lead to asset downtime or failure. This optimizes asset performance and extends their lifecycle.
- Analytical Reporting: SAP ERP Suite offers robust analytical reporting capabilities, providing insights into asset performance, utilization, and maintenance needs. These insights help organizations make informed decisions to enhance asset management strategies.
- Integrated Materials, Assets, and Costing Management: By managing materials, assets, and costs in one place, the suite eliminates the need for multiple systems and manual data entry. This reduces errors and increases productivity, giving organizations a complete view of their assets and associated costs.
Kissflow
Kissflow Finance and Operations Cloud is a powerful software solution designed to streamline and automate business processes. It offers a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users without extensive training or technical knowledge. The software provides flexibility in customization and adaptability, catering to the specific needs of different industries and organizations, and ensures a consistent user experience across both desktop and mobile devices.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: The platform is designed with an intuitive interface that ensures easy navigation and utilization, reducing the need for extensive training or technical expertise.
- Flexibility and Customization: Kissflow offers robust customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the software to meet their specific needs. This adaptability ensures that the software can be effectively used across various industries.
- Consistent User Experience Across Devices: The software provides a seamless experience across desktop and mobile devices, enabling users to access and manage their tasks efficiently, regardless of their location.
- Asset and Facility Management: The platform includes tools to efficiently handle asset and facility management tasks. Users can track and manage assets, conduct maintenance activities, and monitor facility-related expenses.
- Financial Management Capabilities: Kissflow Finance and Operations Cloud offers comprehensive financial management features, including budgeting, expense tracking, invoicing, and financial reporting. These capabilities help organizations manage their finances effectively.
IFS Ultimo
IFS Ultimo is a powerful software solution that offers a wide range of features and functionalities to businesses across various industries. It excels in comprehensive asset management, maintenance planning, and supply chain management. IFS Ultimo is particularly beneficial for industries such as manufacturing, energy, and utilities, where effective asset management and streamlined operations are crucial.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Asset Management: The asset management module efficiently tracks and manages all assets throughout their lifecycle. This feature allows companies to optimize asset utilization, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of their assets. The intuitive user interface and robust reporting capabilities provide accurate, real-time data on asset performance, maintenance history, and costs.
- Maintenance Planning: IFS Ultimo’s maintenance planning module enables companies to effectively schedule and execute preventive and corrective maintenance tasks. It automates work orders, assigns tasks to technicians, and ensures compliance with industry regulations. This minimizes equipment breakdowns, reduces repair costs, and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Supply Chain Management: The supply chain management module simplifies inventory management, procurement, and order fulfillment processes. It optimizes inventory levels, streamlines purchasing activities, and enables seamless collaboration with suppliers. This results in improved supply chain visibility, shorter lead times, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
eMaint
eMaint is a leading Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software designed to provide efficient maintenance management solutions. It offers a comprehensive suite of features and functionalities that enable businesses to effectively schedule and track maintenance activities, optimize equipment performance, and minimize downtime.
Key Features:
- Work Order Management: eMaint provides a comprehensive work order management system that allows users to create, assign, and track work orders from initiation to completion. This feature streamlines the maintenance process, ensuring timely resolution of issues and improved productivity.
- Inventory Management: The software includes robust inventory management capabilities, enabling users to accurately track and control their inventory levels. eMaint offers real-time visibility into inventory, automates the procurement process, and helps organizations avoid stockouts and overstocking.
- Reporting and Analytics: eMaint is equipped with powerful reporting and analytics tools. Users can generate detailed reports on maintenance activities, work orders, inventory, and procurement. These reports provide valuable insights into equipment performance, maintenance costs, and overall maintenance effectiveness, facilitating data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency improvements.
Asset Panda
Asset Panda‘s asset tracking software is an invaluable tool designed to enhance asset management in the manufacturing industry. It provides manufacturers with a comprehensive and customizable solution to efficiently track and manage their assets.
Key Features:
- Customizable Features: Asset Panda allows manufacturers to tailor the software to meet their specific asset-tracking needs. Users can add custom fields, create unique labels, and configure workflows to match their manufacturing processes. This flexibility ensures that the system aligns perfectly with the business requirements of each manufacturer.
- Mobile Apps: The software includes mobile applications that provide a seamless asset management experience. These apps enable manufacturers to access the software on the go, allowing them to easily track and manage assets from anywhere at any time. This mobility is particularly advantageous on the manufacturing floor, where assets are constantly moving and being used.
- Unlimited User Access: Asset Panda offers unlimited user access, allowing all relevant stakeholders within the manufacturing organization to access the software. This feature ensures transparency and collaboration, as the production team, maintenance crew, and quality control personnel all have real-time access to asset information and can contribute to asset management efforts.
Atera
Atera is a cutting-edge software platform designed to revolutionize remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions for IT technicians worldwide. This all-in-one platform provides a comprehensive suite of tools essential for efficient IT management and support.
Key Features:
- Advanced Ticketing System: Atera’s ticketing system streamlines and automates the process of managing customer support requests. It ensures quick response times and efficient issue resolution by allowing IT technicians to track and prioritize customer inquiries, assign tickets to appropriate team members, and update ticket statuses in real time.
- Powerful Asset Management: The platform offers robust asset management capabilities, enabling IT technicians to track and monitor all customer assets, including hardware and software. Through an intuitive and centralized dashboard, technicians can manage warranties, monitor software licenses, and track hardware health, ensuring no critical assets are overlooked.
- Proactive Monitoring Functionalities: Atera provides real-time insights into the performance and health of customer systems through its proactive monitoring capabilities. This feature allows IT technicians to detect and address issues before they escalate, reducing downtime and minimizing the impact on customers’ business operations.
Freshservice
Freshservice is a comprehensive software platform designed to streamline IT service management processes. It provides a robust suite of features and functionalities that help organizations effectively manage their IT services, focusing on ticketing, asset management, and automation.
Key Features:
- Ticketing System: Freshservice’s ticketing system allows users to easily create, track, and manage support tickets. This system facilitates efficient communication and collaboration between IT teams and end-users, ensuring timely resolution of issues. Additionally, the self-service portal empowers users to find solutions to common problems independently, reducing the volume of tickets raised.
- Asset Management: The platform provides a centralized database to track and manage IT assets, including hardware, software licenses, and contracts. This feature helps IT teams optimize asset utilization, track warranty periods, and streamline the procurement process, ensuring all assets are accounted for and efficiently managed.
- Automation Features: Freshservice offers automation functionalities such as workflows and escalation rules to automate routine tasks and ensure adherence to service level agreements (SLAs). This reduces manual efforts and enhances efficiency, allowing IT teams to focus on more critical tasks.
Best Practices for Using Asset Management Software
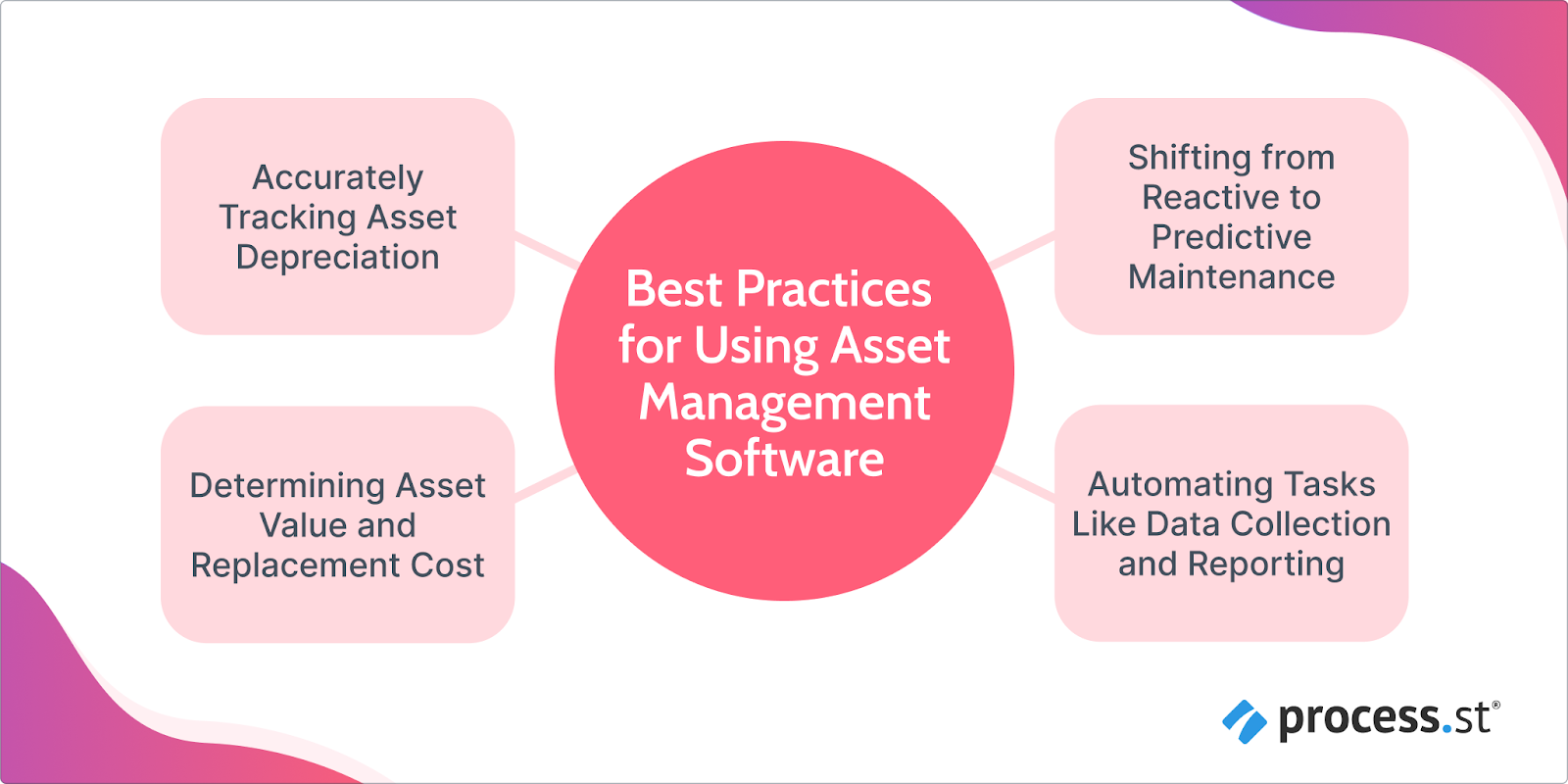
Incorporating best practices in asset management software usage empowers companies to better manage their assets, optimize their lifespan, and make informed decisions about replacement or maintenance.
Here are some of the most effective best practices to keep in mind when using asset management software:
Establishing an Asset Register
Establishing an asset register is essential. This entails compiling a comprehensive list of organizational assets, including necessary details such as their location, condition, purchase date, and maintenance history. Maintaining an accurate asset register ensures that all assets are accounted for.
Accurately Tracking Asset Depreciation
Accurately tracking asset depreciation is another vital practice. Asset management software should have the capability to monitor asset value over time, factor in depreciation, and provide real-time updates on an asset’s current worth. This allows organizations to make informed decisions regarding asset replacement or repair.
Determining Asset Value and Replacement Cost
Determining asset value and replacement cost is equally important. Asset management software should provide functionalities to assess the current value of assets and estimate their replacement cost. This information aids in budgeting for asset maintenance, repairs, or future acquisitions.
Shifting from Reactive to Predictive Maintenance
Shifting from reactive to predictive maintenance is a recommended best practice. Asset management software is equipped with predictive maintenance features that leverage real-time data to identify potential issues or breakdowns before they occur. By adopting predictive maintenance strategies, organizations can minimize downtime, optimize asset performance, and reduce costs.
Automating Tasks Like Data Collection and Reporting
Automating tasks like data collection and reporting enhances operational efficiency. Asset management software should have the capability to automate data collection, analyze information, and generate accurate reports. This streamlines the asset management process, saving time and resources.
Key Features of Asset Management Process Automation Software
Asset management process automation software is designed to streamline the management of assets within an organization. Here are some of the key features of asset management software you should consider when picking a tool for your organization:
Maintaining a Detailed Record of Assets
Asset management process automation software allows users to track and monitor the status, location, and condition of each asset, ensuring accurate inventory management. This feature enables organizations to easily identify and allocate resources effectively.
Automating Operational Workflows
The software provides standardized processes for asset check-in and checkout, allowing for efficient tracking and managing of assets. It also enables users to easily reserve assets, reducing conflicts and improving availability.
Maintenance Scheduling
Maintenance scheduling is a key feature that allows organizations to schedule routine maintenance tasks, such as inspections, repairs, and replacements, ensuring assets remain in optimal condition. This helps prevent asset downtime and extends their lifespan.







