Get work done right, and right-on-time with our industry leading BPM platform.
A Complete Guide to Business Process Management (BPM)
Organizations of all sizes must continually adapt to new market demands, technological advancements, and customer expectations. This is where business process management (BPM) comes into play.
BPM is a systematic approach to optimizing, automating, and improving an organization’s processes to drive efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the fundamentals of BPM, its importance in modern businesses, key benefits, and practical applications across various industries.
Whether you are looking to streamline operations, increase productivity, or boost customer satisfaction, understanding BPM is essential for achieving sustainable growth and long-term success.
- What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
- Types of Business Processes
- Benefits of Business Process Management
- What Are the 5 Stages of the BPM Lifecycle?
- Practical Examples of Business Process Management
- Business Process Automation: Identifying Repetitive Tasks
- Business Process Management Best Practices
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach taken by organizations to optimize and streamline their business processes. It involves identifying, documenting, analyzing, and improving processes to achieve operational efficiency and meet organizational goals.
BPM encompasses the management of both ongoing and repetitive tasks, as well as the integration of automation technologies and software systems to enhance workflow management. By implementing BPM, businesses can:
- Enhance customer satisfaction
- Achieve continuous improvement
- Drive digital transformation
BPM can be either human-centric or integration-centric, depending on the level of human involvement in the process. It can also be either document-centric or software-centric, depending on the focus of the BPM tools used.
Overall, BPM aims to improve process efficiency, increase productivity, and enhance the overall performance of an organization.
Types of Business Processes
Business processes are essential to the success of any organization, providing a structured approach to achieving goals and driving efficiency. By understanding and optimizing these processes, companies can improve productivity, customer satisfaction, and overall performance. This article will explore the three main types of business processes: primary, secondary, and management processes.
Primary Business Processes
Primary processes refer to the core activities that directly contribute to the production and delivery of a company’s products or services. These processes are critical to satisfying customer needs and achieving the business’s main objectives. Key examples of primary processes include:
- Production
- Sales
- Customer service
By optimizing these primary processes, businesses can enhance value creation and ensure customer satisfaction, which is vital for long-term success.
Secondary Business Processes
Secondary processes support the primary activities by providing essential functions that ensure smooth daily operations. While these processes do not directly contribute to product or service delivery, they are crucial for the business’s operational effectiveness. Examples of secondary processes include:
- Human resources
- Finance
- IT support
These processes help maintain the infrastructure needed for primary processes to run efficiently, making them indispensable for overall organizational performance.
Management Business Processes
Management processes focus on the strategic oversight of both primary and secondary processes. They involve planning, organizing, and controlling the various activities within the organization to achieve strategic goals. Important management processes include:
- Strategic planning
- Performance management
- Budgeting
Through effective management processes, businesses can align their operations with their goals, ensure resource allocation, and continuously improve their overall efficiency.
Benefits of Business Process Management
Business Process Management (BPM) offers a wide range of advantages for organizations aiming to enhance their efficiency, productivity, and adaptability. By implementing effective BPM strategies, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, improve product and service quality, and respond more swiftly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Increased Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of BPM is the optimization of business processes. By automating repetitive tasks and eliminating bottlenecks, BPM helps organizations complete tasks faster and more effectively. This increased efficiency reduces resource wastage and minimizes the time required to complete core processes, resulting in significant cost savings.
Enhanced Productivity
BPM improves productivity by providing employees with clear, structured workflows. This ensures that tasks are executed consistently and efficiently across the organization. By streamlining processes, BPM also allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks rather than getting bogged down by inefficiencies.
Cost Reduction
Through process optimization, BPM helps organizations cut down on unnecessary expenses. Whether through the reduction of manual tasks, faster process completion, or improved resource allocation, BPM helps lower operational costs while maintaining or enhancing service quality.
Improved Agility
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, agility is essential. BPM provides businesses with the flexibility to quickly adapt their processes to meet new market demands, technological advancements, or evolving customer expectations. By allowing for easy modifications to workflows, BPM enables organizations to stay competitive and seize new opportunities.
Higher Quality Products and Services
With continuous process monitoring and improvement, BPM contributes to the enhancement of product and service quality. By ensuring that processes are executed correctly and consistently, BPM reduces the likelihood of errors, improves compliance with industry standards, and ultimately increases customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Competitive Advantage
Organizations that embrace BPM can differentiate themselves from competitors by delivering faster, higher-quality services at a lower cost. BPM supports continuous improvement, enabling businesses to maintain a competitive edge by optimizing their operations and exceeding customer expectations.
What Are the 5 Stages of the BPM Lifecycle?
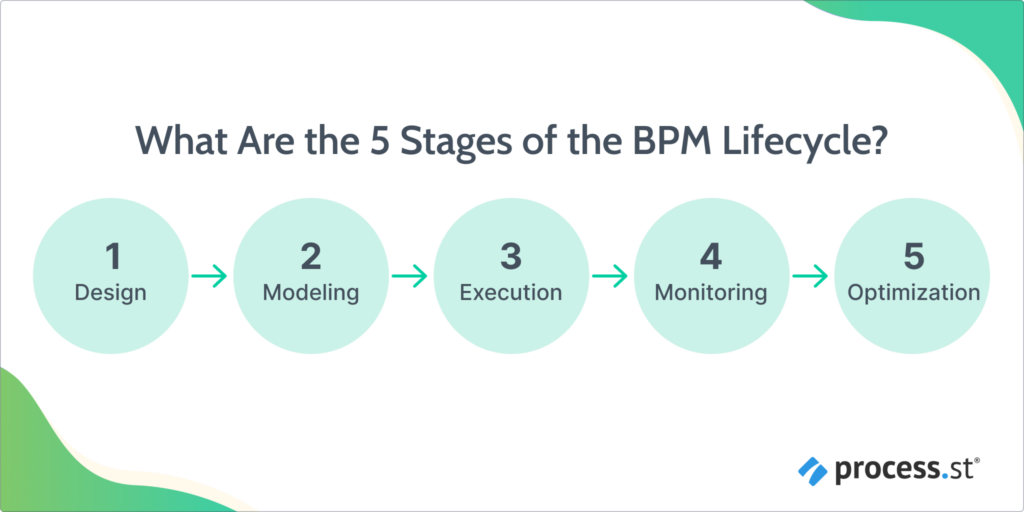
The business process management lifecycle consists of five key stages that guide organizations in systematically managing, optimizing, and improving their processes. These stages help businesses identify inefficiencies, implement improvements, and ensure continuous performance optimization. Here are the five stages of the BPM lifecycle:
1. Design
In the design phase, organizations define and document the processes that need to be managed or improved. This includes mapping out the current processes (as-is) and designing the ideal future state (to-be) processes. During this stage, key factors such as process flow, task responsibilities, and performance metrics are considered.
Key activities include:
- Process modeling and mapping
- Identifying bottlenecks or inefficiencies
- Establishing performance criteria and outcomes
2. Modeling
The modeling phase involves creating a detailed representation of the designed process. Here, businesses simulate different scenarios to test how changes will affect performance. This phase helps visualize how the process will work under various conditions, such as changes in volume, deadlines, or resource availability.
Key activities include:
- Simulating different workflows
- Testing variables such as time, cost, and resource allocation
- Analyzing potential outcomes to optimize process flows
3. Execution
In the execution phase, the modeled process is put into practice. This stage may involve implementing new technologies, automating certain tasks, or updating workflows to align with the newly designed processes. BPM software often plays a critical role in automating and managing these processes in real time.
Key activities include:
- Implementing the designed process
- Automating tasks using BPM tools or software
- Ensuring all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities
4. Monitoring
The monitoring phase focuses on tracking the performance of the executed process. This involves continuously measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the process. By closely monitoring, organizations can quickly identify issues, inefficiencies, or deviations from expected outcomes.
Key activities include:
- Tracking KPIs such as time, cost, and output quality
- Identifying process bottlenecks or issues
- Using BPM software for real-time monitoring and analytics
5. Optimization
In the optimization phase, organizations use the insights gained from monitoring to refine and improve the process. The goal is to make ongoing adjustments that enhance performance, eliminate inefficiencies, and ensure the process is adaptable to new challenges. This stage often involves iterative improvements and continuous feedback loops to maintain optimal performance.
Key activities include:
- Identifying areas for improvement based on performance data
- Making process adjustments to increase efficiency and effectiveness
- Continuously seeking ways to improve and streamline workflows
Practical Examples of Business Process Management
Business process management plays a crucial role in helping organizations optimize their workflows, automate repetitive tasks, and improve overall efficiency. By streamlining business processes, companies can achieve better results, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are some practical examples of different business processes that benefit from BPM:
Sales Process
The sales process encompasses all activities related to selling products or services. BPM can automate and streamline steps such as:
- Lead generation and management
- Prospecting and customer outreach
- Presenting offers and proposals
- Negotiating deals and closing sales
By integrating customer relationship management (CRM) tools and automating follow-ups, BPM enhances the sales team’s efficiency, reduces response times, and improves customer engagement.
Procurement Process
The procurement process involves acquiring goods or services from external suppliers. BPM software helps optimize steps like:
- Vendor selection based on performance and pricing
- Price negotiation and contract management
- Purchase order creation and approval workflows
- Product delivery and inventory updates
BPM ensures seamless coordination between departments, reduces errors in ordering, and keeps track of spending for better budgeting and cost control.
Customer Service Process
Effective customer service is critical for any organization. BPM helps automate and monitor the customer service process, which includes:
- Responding to customer inquiries quickly through automated ticketing systems
- Resolving complaints with defined workflows
- Tracking customer satisfaction through surveys and performance metrics
By automating these tasks and using BPM dashboards for real-time insights, organizations can improve response times, ensure customer satisfaction, and maintain service quality across all channels.
Hiring Process
The hiring process involves finding and recruiting new employees. BPM streamlines tasks such as:
- Posting job openings across platforms
- Screening resumes using automated filters
- Scheduling interviews and conducting background checks
- Onboarding new employees with a structured plan
With BPM, HR teams can reduce time-to-hire, improve candidate communication, and ensure compliance with hiring regulations.
Financial Process
The financial process deals with managing a company’s finances. BPM can enhance workflows in areas like:
- Budgeting with real-time updates and approval hierarchies
- Accounting by automating data entry, invoice processing, and audits
- Financial reporting with auto-generated reports based on the latest data
BPM ensures accurate financial tracking, minimizes errors in accounting, and facilitates compliance with financial regulations.
Business Process Automation: Identifying Repetitive Tasks
Identifying repetitive tasks in a business process is essential for driving efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling automation. By pinpointing these tasks, organizations can streamline operations, eliminate bottlenecks, and boost overall productivity. Business process management plays a pivotal role in analyzing processes to uncover areas where automation can create significant improvements.
Examples of repetitive tasks in key business processes:
- Sales Process: In the sales process, lead generation is a prime example of a repetitive task. Sales teams often spend considerable time manually sourcing and qualifying leads. BPM software can automate this through CRM systems and targeted marketing campaigns, reducing manual effort and enabling teams to focus more on closing deals rather than sourcing them.
- Procurement Process: In procurement, tasks such as vendor selection and price negotiation are repetitive. BPM tools can automate the supplier evaluation, bidding, and contract management processes, helping companies quickly identify the best vendors at competitive prices while reducing time spent on repetitive decision-making.
- Customer Service Process: Customer support often deals with repetitive inquiries. For example, responding to frequently asked questions (FAQs) or handling similar customer complaints. BPM tools can automate responses using chatbots and automated ticketing systems, improving response time and reducing manual effort.
- Order Fulfillment Process: A well-known example is Amazon’s implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in its order fulfillment centers. By automating repetitive tasks like inventory picking, packing, and shipment tracking, Amazon significantly improved operational efficiency, reduced errors, and handled higher order volumes with fewer human resources.
By leveraging BPM to identify and automate repetitive tasks, organizations free up valuable resources, reduce operational costs, and create more agile and efficient processes. This allows businesses to focus on value-added activities, improve their competitive advantage, and ultimately drive business growth.
Business Process Management Best Practices

To ensure successful implementation and long-term benefits of Business Process Management (BPM), businesses should adopt proven best practices that promote efficiency, adaptability, and continuous improvement. Here are some key BPM best practices:
Understand and Document Current Processes
Before making any changes, it’s critical to understand the existing processes. Thoroughly document the current workflows, responsibilities, and performance metrics to create a baseline for future improvements.
Align BPM with Business Goals
BPM initiatives should be aligned with the overall business strategy and objectives. The goal of process improvement should directly support key business outcomes, such as increasing efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, or reducing costs.
Involve Key Stakeholders
Engage all stakeholders, from process owners and employees to leadership and customers. This ensures that everyone affected by process changes is informed, involved in decision-making, and aligned with the goals of BPM initiatives.
Focus on Continuous Improvement
BPM is not a one-time project but a continuous effort. Regularly review and update processes to reflect changing market conditions, customer needs, and new technologies. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the effectiveness of processes.
Automate Where Possible
Identify repetitive, manual, and time-consuming tasks that can be automated. Automation reduces human error, increases efficiency, and allows employees to focus on high-value tasks.
Leverage BPM Software
Utilize BPM software to streamline processes, manage workflows, and monitor performance. BPM tools allow for real-time monitoring and analytics, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.







